Table of Contents
1. Introduction
Nicotine is often associated with cigarettes and tobacco products, but it’s also found in vapes, nicotine pouches, and other delivery methods. While some believe it’s “just a stimulant,” nicotine has numerous harmful effects on health. This article explores why nicotine is considered dangerous, detailing its physical, mental, and societal impacts. Whether you’re considering quitting or are curious about its effects, this guide offers valuable insights.
2. What is Nicotine?
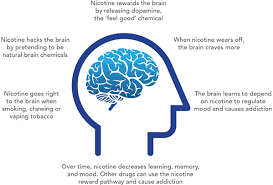
Nicotine is an alkaloid found naturally in the tobacco plant and in trace amounts in certain vegetables like tomatoes and eggplants. As a stimulant, it impacts the central nervous system, increasing heart rate and stimulating dopamine release, which can make users feel alert and relaxed. However, its addictive potential and wide-ranging effects on the body make it more harmful than many people realize.
3. How Nicotine Affects the Body
Nicotine affects various systems within the body, which can lead to both short-term and long-term health issues.
3.1. The Cardiovascular System
Nicotine increases blood pressure and heart rate, which places strain on the cardiovascular system. This can contribute to heart disease, increase the risk of heart attacks, and cause circulation problems over time.
3.2. The Respiratory System
Although nicotine itself doesn’t directly damage lung tissue, it is often inhaled through cigarettes or vapes that contain harmful chemicals. This exposure can lead to chronic respiratory diseases, including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and lung cancer.
3.3. The Digestive System
Nicotine can impact the digestive system by increasing acid production in the stomach, leading to acid reflux, ulcers, and even gastrointestinal distress.
3.4. The Reproductive System
Nicotine can affect fertility and reproductive health. For pregnant women, nicotine exposure can lead to complications such as low birth weight, premature birth, and developmental issues in the fetus.
By impacting multiple systems, nicotine poses risks beyond just addiction, making it important to understand its widespread effects.
4. The Health Risks of Nicotine
Using nicotine regularly is linked to various health risks. Here are some of the primary dangers associated with nicotine:
4.1. Increased Risk of Heart Disease
Nicotine raises blood pressure and narrows blood vessels, which can increase the risk of developing heart disease. Long-term nicotine users are significantly more likely to suffer from heart attacks and strokes.
4.2. Potential for Cancer
While nicotine itself is not a carcinogen, it is often consumed with tobacco products that contain carcinogenic chemicals. This exposure is linked to cancers of the lung, mouth, throat, and more.
4.3. Respiratory Diseases
Inhaling nicotine through smoking or vaping exposes the lungs to toxic chemicals that can damage lung tissue and lead to diseases like emphysema, bronchitis, and COPD.
4.4. Impact on Brain Health
Nicotine can affect brain development in young people and increase the risk of cognitive impairment. It also has been linked to mood disorders, such as anxiety and depression, especially in long-term users.
The health risks associated with nicotine consumption highlight the importance of considering safer alternatives or support systems for those aiming to quit.
5. Psychological and Behavioral Impact of Nicotine
Nicotine’s effects are not limited to physical health; it also significantly impacts mental well-being and behavior.
5.1. Increased Anxiety and Stress
Many people believe nicotine relieves stress, but studies show it may actually increase anxiety and stress levels over time. Dependency on nicotine can make users feel more anxious during withdrawal, leading to a cycle of reliance.
5.2. Mood Swings and Irritability
Nicotine withdrawal is linked to irritability, mood swings, and feelings of restlessness. For those trying to quit, these symptoms can be intense, making it challenging to stay nicotine-free.
5.3. Impact on Concentration and Mental Health
Nicotine can cause temporary increases in focus and alertness, but long-term use often impairs mental clarity and can lead to addiction-driven anxiety and depression. Dependency on nicotine also impacts cognitive performance, especially when the body craves nicotine.
6. Nicotine’s Impact on Adolescents and Young Adults
Nicotine is particularly harmful to young users due to its effects on the developing brain. Adolescents and young adults are at risk of lifelong dependency and other health issues if they start using nicotine early.
6.1. Impact on Brain Development
The human brain continues developing into the mid-20s, and nicotine exposure during adolescence can interfere with this process. Nicotine can impair areas related to memory, concentration, and impulse control, leading to long-term cognitive and behavioral changes.
6.2. Increased Likelihood of Addiction
Young people are more susceptible to addiction because their brains are still forming reward and pleasure pathways. Nicotine addiction at a young age often leads to lifelong dependency, increasing health risks over time.
6.3. Gateway to Other Substances
Studies have shown that adolescents who start with nicotine are more likely to experiment with other addictive substances. The initial addiction to nicotine can make them more vulnerable to future substance use.
For adolescents and young adults, avoiding nicotine is essential to safeguard mental and physical health as well as future well-being.
7. The Social and Economic Costs of Nicotine Addiction
Beyond individual health effects, nicotine use can also lead to significant social and economic consequences.
7.1. Financial Burden
Regular nicotine use can become a costly habit. For long-term smokers or vapers, the expense can accumulate over the years, placing financial strain on individuals and families.
7.2. Impact on Relationships
Nicotine addiction can affect relationships due to mood swings, irritability, and the prioritization of nicotine over social interactions. Loved ones may feel the impact of addiction, especially when trying to support someone through quitting.
7.3. Societal Health Costs
Nicotine-related health issues place a burden on healthcare systems globally. Treating diseases caused by smoking, vaping, and other nicotine products costs billions in medical care, reducing funds available for other health needs.
Addressing nicotine addiction not only benefits the individual but also has a positive impact on society as a whole.
8. FAQs
1. Is nicotine dangerous if it doesn’t come from cigarettes?
Nicotine on its own is still addictive and harmful to cardiovascular health, even if it’s not consumed through smoking. However, cigarettes add extra toxins that increase the risk of diseases.
2. Why is nicotine addictive?
Nicotine triggers the release of dopamine, creating a pleasurable feeling that reinforces use. Over time, the brain becomes dependent on nicotine to release dopamine, leading to addiction.
3. Can nicotine affect my mental health?
Yes, nicotine can exacerbate stress, anxiety, and depression, particularly during withdrawal. Long-term use may impair brain function and increase mood-related issues.
4. Are e-cigarettes a safer way to consume nicotine?
While e-cigarettes eliminate the combustion products of traditional cigarettes, they still expose users to addictive nicotine and other potentially harmful chemicals.
5. What’s the best way to quit nicotine?
Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT), prescription medications, behavioral counseling, and support groups are all effective tools for quitting. Choosing a combination of methods often yields the best results.
Understanding why nicotine is bad can empower users to make informed decisions about its use and consider pathways to quit if they seek a healthier lifestyle. For those exploring alternatives or seeking nicotine-free options, SnuffMint offers a variety of products, and support is available via WhatsApp at +852-90568182.