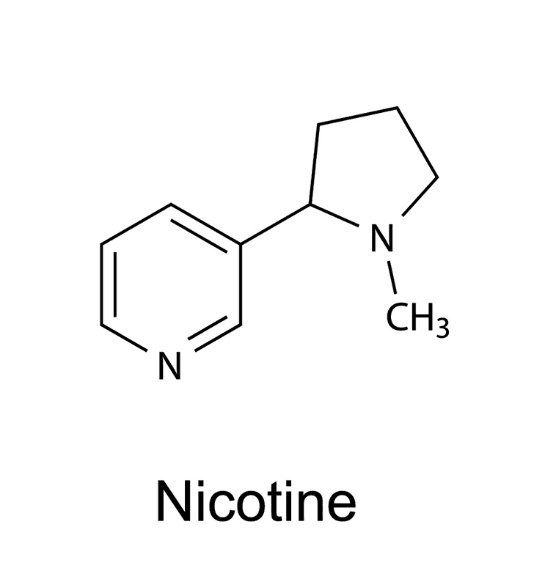
Nicotine is a well-known stimulant found in tobacco products, including cigarettes and nicotine pouches. While many users seek out nicotine for its stimulating effects, some individuals experience headaches as a side effect. This blog post explores the reasons why nicotine can trigger headaches, the different types of headaches associated with nicotine use, and tips for managing or preventing these headaches.
Understanding Nicotine
Before delving into how nicotine can cause headaches, it’s essential to understand what nicotine is and how it affects the body. Nicotine is an alkaloid that acts on the central nervous system, influencing various neurotransmitters, such as dopamine and norepinephrine. These changes can lead to increased alertness, improved mood, and heightened cognitive function, which is why many people turn to nicotine for a quick boost.
However, just as nicotine can produce positive effects, it can also have adverse reactions. One common complaint among users is headaches.
Types of Headaches Associated with Nicotine
There are generally two types of headaches that may be linked to nicotine: tension headaches and migraines.

Tension Headaches
Tension headaches are the most common type of headache and are often triggered by stress, anxiety, fatigue, and muscle tension. Nicotine can contribute to tension headaches in several ways:
- Vasoconstriction: Nicotine causes blood vessels to constrict, which can lead to reduced blood flow to the brain. This change can trigger tension headaches, especially if the user is already prone to muscle tension or stress.
- Withdrawal Symptoms: For regular nicotine users, the absence of nicotine can lead to withdrawal symptoms, including tension headaches. If a person who regularly consumes nicotine goes without it for an extended period, the body may react negatively, resulting in a headache.
- Dehydration: Nicotine has a diuretic effect, meaning it can lead to increased urination. This can result in dehydration, which is another common trigger for tension headaches.
Migraines
Migraines are more severe headaches characterized by intense pain, often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound. Several factors connect nicotine use and migraines:
- Chemicals in Tobacco: Beyond nicotine, tobacco smoke contains numerous chemicals that can exacerbate migraine triggers. The inhalation of smoke can irritate the nasal passages and sinuses, leading to headaches.
- Variability in Dosage: Different forms of nicotine deliver varying amounts of the substance to the bloodstream. Sudden spikes or drops in nicotine levels—common with switching from cigarettes to nicotine pouches or vice versa—can trigger migraines in susceptible individuals.
- Hormonal Influence: Some research suggests that nicotine may interact with hormonal pathways that can provoke migraines. Women, in particular, may notice an increase in migraine frequency during certain menstrual cycles when using nicotine.
Factors Influencing Nicotine-Induced Headaches
Several factors can influence whether an individual experiences headaches while using nicotine:
- Individual Sensitivity: Everyone’s body reacts differently to substances, including nicotine. Some people may be more sensitive to nicotine than others, making them more likely to experience headaches.
- Frequency of Use: Regular nicotine users may develop a tolerance to its stimulating effects. However, this can create a cycle where decreased intake leads to withdrawal headaches, making it crucial for users to manage their consumption carefully.
- Other Substances: Combining nicotine with other substances—such as alcohol, caffeine, or certain medications—can increase the likelihood of developing headaches. For instance, excessive caffeine can lead to dehydration, exacerbating the effects of nicotine.
- Underlying Health Conditions: Individuals with pre-existing health conditions, such as hypertension or anxiety disorders, may find that nicotine exacerbates their symptoms, leading to headaches. It’s essential to consider overall health when evaluating the impact of nicotine.
Tips for Managing Nicotine-Induced Headaches
If you’re experiencing headaches related to nicotine use, there are several strategies you can employ to manage or prevent them:
- Stay Hydrated: Since nicotine can lead to dehydration, it’s crucial to drink plenty of water throughout the day. Staying hydrated can help mitigate headaches caused by both tension and dehydration.
- Monitor Your Consumption: Keep track of your nicotine intake and assess how it correlates with your headache patterns. Gradually adjusting your usage may help reduce headache frequency.
- Switch to Alternative Products: If you find traditional tobacco products trigger headaches, consider exploring alternative nicotine delivery methods, such as nicotine pouches or gums. These options may offer a different experience that could be less likely to induce headaches.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Incorporating relaxation techniques, such as mindfulness meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises, can help reduce stress and tension that may contribute to headaches.
- Limit Alcohol and Caffeine: Reducing the consumption of alcohol and caffeine can lessen the likelihood of dehydration and minimize potential headache triggers.
- Practice Good Sleep Hygiene: Ensure that you are getting enough sleep each night and maintaining a consistent sleep schedule. Poor sleep can trigger both tension headaches and migraines, so aim for 7-9 hours of quality rest.
- Consult with a Healthcare Professional: If headaches persist or worsen despite trying to manage your nicotine intake and overall health, it may be beneficial to speak with a healthcare professional. They can help identify underlying issues and suggest appropriate treatments or alternatives.
- Consider Over-the-Counter Medications: Non-prescription pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, may help alleviate headaches when they occur. However, use these medications sparingly and follow the recommended dosages to avoid rebound headaches.
Understanding Withdrawal Headaches
For those attempting to quit nicotine, withdrawal symptoms can include intense headaches. These headaches are often a sign that the body is adjusting to the absence of nicotine. Here are some key points regarding withdrawal headaches:
- Symptoms Duration: Withdrawal headaches typically peak within the first few days after quitting and may last up to several weeks as the body adjusts. The intensity and duration can vary greatly among individuals.
- Managing Withdrawal: Gradually reducing nicotine intake rather than quitting abruptly can help mitigate withdrawal headaches. Nicotine replacement therapies (NRTs), such as nicotine pouches, can offer a controlled way to decrease nicotine levels in the body.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Maintaining a balanced diet, regular exercise, and good hydration during the withdrawal period can help reduce withdrawal symptoms, including headaches.
Final Thoughts
Nicotine can provide short-term stimulation and mood enhancement, but it can also lead to negative side effects like headaches. Understanding the connection between nicotine consumption and headache types—tension and migraine—can empower users to make informed choices about their nicotine use.
By recognizing individual sensitivity to nicotine, monitoring consumption patterns, and employing strategies to manage headaches, users can potentially avoid or alleviate this discomfort. Additionally, if headaches persist or become debilitating, seeking professional advice is crucial to ensure overall health and well-being.
Ultimately, whether you’re a long-time user of nicotine products or considering them for the first time, understanding your body’s reactions and making educated decisions can enhance your experience while minimizing adverse effects. Nicotine use should always be approached mindfully, and when in doubt, consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice and support.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1141358432-088ec597f8be4f3db1b0a966e346b840.jpg)
Lifestyle Changes to Reduce Headaches
In addition to the strategies already mentioned, certain lifestyle changes can further help mitigate the occurrence of nicotine-induced headaches. Here are some additional tips that can contribute to overall wellness and headache prevention:
- Maintain a Balanced Diet: Eating a nutrient-rich diet can support brain health and potentially reduce headache frequency. Focus on consuming whole foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals. Foods such as leafy greens, nuts, seeds, fatty fish, fruits, and whole grains can all be beneficial.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in regular exercise can help reduce stress, improve mood, and alleviate tension headaches. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous activity each week, along with muscle-strengthening exercises on two or more days.
- Limit Trigger Foods: Some foods and beverages are known migraine triggers for many individuals. Common culprits include aged cheeses, processed meats, caffeine, chocolate, and alcohol. Keeping a food diary can help identify specific triggers.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress is a significant trigger for both tension headaches and migraines. Incorporating stress management techniques—such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, tai chi, or spending time in nature—can bring about relaxation and reduce the likelihood of headaches.
- Stay Consistent with Meals: Skipping meals or having irregular eating patterns can lead to drops in blood sugar levels, triggering headaches. Aim to eat balanced meals and snacks throughout the day to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
- Avoid Strong Odors and Environmental Triggers: Certain smells, such as strong perfumes, chemical fumes, or smoke, can trigger headaches in susceptible individuals. Being mindful of your environment and avoiding these triggers can be helpful.
- Set Up an Ergonomic Workspace: If you work at a desk or spend extended periods on the computer, ensure that your workspace is ergonomically designed. Poor posture can lead to tension headaches. Adjust your chair, monitor height, and keyboard position to promote good posture.
- Consider Acupuncture or Massage Therapy: Some individuals find relief from headaches through alternative therapies. Acupuncture and massage therapy can help alleviate tension and promote relaxation, which may reduce the frequency and intensity of headaches.
Seeking Professional Guidance
If headaches persist despite implementing these lifestyle changes, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional who specializes in headache disorders or pain management. They can conduct a thorough evaluation and recommend personalized treatment plans. Possible treatments include:
- Prescription Medications: For frequent migraines or severe headaches, doctors may prescribe medications specifically designed to prevent migraines or provide relief during an attack.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): This form of therapy can help individuals manage stress, change negative thought patterns, and develop coping strategies for dealing with headaches.
- Botox Injections: For chronic migraine sufferers, Botox injections have been shown to be an effective preventive treatment.
- Dietary Supplements: Certain supplements, such as magnesium, riboflavin (Vitamin B2), and Coenzyme Q10, have been studied for their potential to reduce the frequency of migraines.
Conclusion
Understanding why nicotine can give you a headache is crucial for anyone who uses or considers using nicotine products. While nicotine has its allure due to its stimulating effects, the potential side effects—particularly headaches—should not be overlooked. By recognizing the connection between nicotine consumption and different types of headaches, users can better navigate their choices and adopt preventative strategies.
From lifestyle and dietary adjustments to consulting with healthcare professionals, there are numerous ways to manage and reduce the occurrence of headaches related to nicotine use. Knowledge about personal responses to nicotine and individual triggers can empower users towards healthier habits and decisions, ultimately fostering a better quality of life.
Embracing a holistic approach to health that emphasizes physical, emotional, and mental well-being can significantly impact how one experiences nicotine and mitigates the associated side effects. Whether you are a long-time user or considering nicotine for the first time, being proactive about your health will contribute to a more informed and balanced lifestyle.